Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is a rare genetic disorder that affects muscle strength and movement, significantly impacting life expectancy. This condition is caused by a mutation in the survival motor neuron 1 (SMN1) gene. Understanding the life expectancy of individuals with SMA requires a deep dive into the types, treatments, and modern advancements that are reshaping the prognosis for patients.
SMA is not just a medical condition but a complex challenge that touches the lives of patients and their families. Advances in research and treatment options have transformed the landscape, offering hope and extending life expectancy for those affected. In this article, we will explore the various factors influencing life expectancy in SMA and provide actionable insights for families and caregivers.
Our goal is to offer comprehensive, evidence-based information to empower individuals with SMA and their loved ones. By understanding the latest developments in care, treatment, and support, we can work toward improving quality of life and extending life expectancy for all individuals affected by this condition.
Read also:Oscar Isaac And Elvira Lind A Journey Through Love Art And Partnership
Table of Contents
- What is SMA?
- Types of SMA
- Life Expectancy Overview
- Factors Affecting Life Expectancy
- Current Treatment Options
- Managing Symptoms
- Role of Genetic Counseling
- Advancements in Research
- Support and Resources
- Conclusion
What is SMA?
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is a neuromuscular disorder characterized by the loss of motor neurons, leading to progressive muscle weakness and atrophy. It is the leading genetic cause of infant mortality, affecting approximately 1 in 10,000 live births. SMA is caused by a mutation in the SMN1 gene, which is responsible for producing the survival motor neuron (SMN) protein. Without sufficient levels of this protein, motor neurons in the spinal cord degenerate, resulting in muscle wasting and impaired movement.
While SMA primarily affects muscle strength and movement, its impact extends to other vital systems, such as breathing and swallowing. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for improving outcomes and extending life expectancy. Advances in genetic testing and therapies have significantly enhanced our ability to manage this condition effectively.
Causes of SMA
SMA is an autosomal recessive disorder, meaning that an individual must inherit two copies of the mutated SMN1 gene—one from each parent—to develop the condition. Approximately 1 in 50 people are carriers of the SMA gene, often without displaying symptoms. Understanding the genetic basis of SMA is essential for accurate diagnosis and family planning.
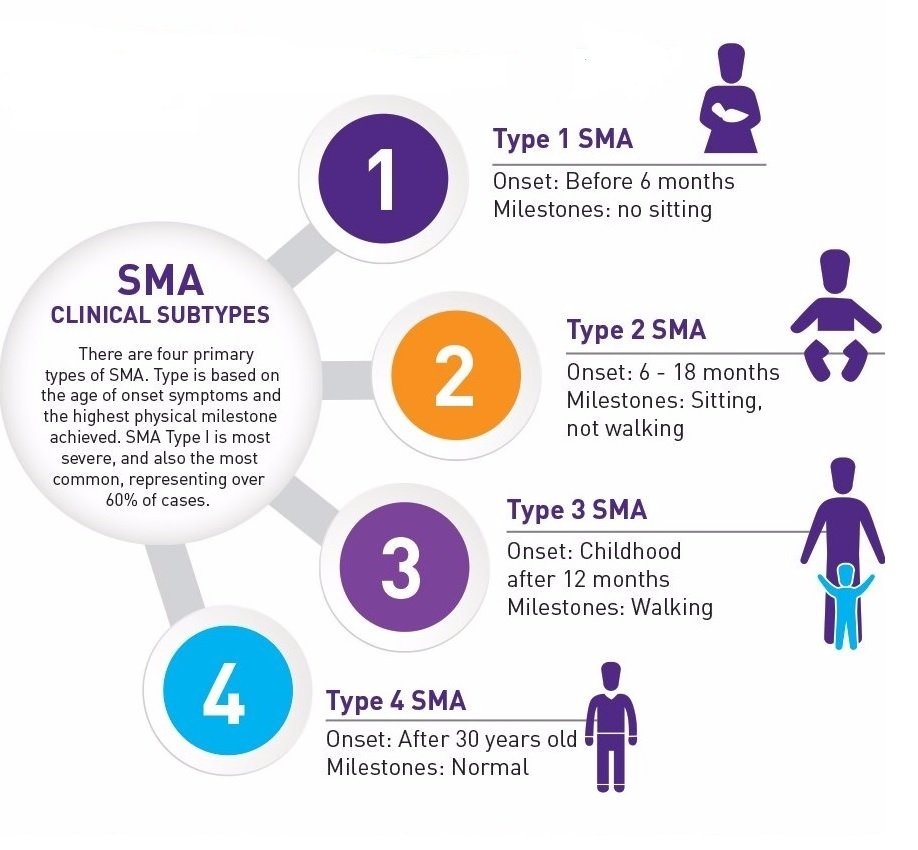
Types of SMA
SMA is classified into several types based on age of onset and severity of symptoms. Each type has distinct characteristics that influence life expectancy and treatment options. Below is a breakdown of the primary types of SMA:
- Type 0 (Prenatal Onset): The most severe form, with symptoms appearing before or shortly after birth.
- Type 1 (Infantile Onset): Also known as Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, this type affects infants under six months old.
- Type 2 (Intermediate SMA): Symptoms typically emerge between six and 18 months of age.
- Type 3 (Juvenile SMA): Also called Kugelberg-Welander disease, this type affects children over 18 months old.
- Type 4 (Adult-Onset SMA): This milder form manifests in adulthood, with slower progression.
Impact of SMA Types on Life Expectancy
The life expectancy of individuals with SMA varies significantly depending on the type and severity of the condition. For example, individuals with Type 1 SMA historically faced the shortest life expectancy, with many not surviving beyond early childhood without intervention. However, recent advancements in treatment have improved outcomes even for the most severe cases.
Life Expectancy Overview
The life expectancy of individuals with SMA has improved dramatically over the past few decades, thanks to advancements in medical care and treatment options. Early diagnosis, access to specialized therapies, and comprehensive supportive care play critical roles in extending life expectancy.
Read also:What Happened To The Iron Claw Brothers A Gripping Story Of Triumph And Tragedy
For individuals with Type 1 SMA, life expectancy has increased from months to years with the introduction of disease-modifying therapies such as nusinersen, onasemnogene abeparvovec, and risdiplam. Similarly, individuals with Types 2 and 3 SMA are now living longer, healthier lives with proper management and care.
Historical vs. Current Life Expectancy
In the past, life expectancy for SMA was bleak, with many individuals not surviving into adulthood. However, modern medicine has transformed the outlook for patients. According to a 2022 study published in the Journal of Neurology, individuals receiving disease-modifying therapies are living longer and experiencing improved quality of life compared to those who do not receive such interventions.
Factors Affecting Life Expectancy
Several factors influence the life expectancy of individuals with SMA, including the type of SMA, access to treatment, and overall health management. Below are some key factors:
- Type of SMA: As mentioned earlier, the type of SMA significantly impacts life expectancy.
- Access to Treatment: Availability of disease-modifying therapies and supportive care can extend life expectancy.
- Genetic Factors: The number of SMN2 gene copies can influence disease severity and prognosis.
- Overall Health Management: Proper nutrition, respiratory care, and physical therapy play vital roles in managing symptoms.
Role of SMN2 Gene Copies
The SMN2 gene produces a small amount of functional SMN protein, which can partially compensate for the loss of SMN1 function. Individuals with more SMN2 copies tend to have milder disease presentations and better outcomes. Understanding this genetic factor is essential for tailoring treatment plans and predicting life expectancy.
Current Treatment Options
Advances in medical science have led to the development of several effective treatments for SMA, each targeting the underlying cause of the condition. These treatments aim to increase SMN protein levels, improve muscle function, and extend life expectancy.
- Nusinersen (Spinraza): An intrathecal injection that modifies RNA splicing to increase SMN protein production.
- Onasemnogene Abeparvovec (Zolgensma): A gene therapy that delivers a functional copy of the SMN1 gene to motor neurons.
- Risdiplam (Evrysdi): An oral medication that enhances SMN2 gene activity to produce more SMN protein.
Effectiveness of Treatments
Clinical trials and real-world evidence demonstrate the effectiveness of these treatments in improving motor function, reducing hospitalizations, and extending life expectancy. For example, a study published in The Lancet found that infants treated with onasemnogene abeparvovec achieved developmental milestones that were previously unattainable for individuals with Type 1 SMA.
Managing Symptoms
In addition to disease-modifying therapies, managing symptoms is crucial for improving quality of life and extending life expectancy in SMA. This involves a multidisciplinary approach, including:
- Respiratory Care: Ensuring proper ventilation and airway management.
- Nutritional Support: Providing adequate nutrition through feeding tubes if necessary.
- Physical Therapy: Maintaining mobility and preventing muscle contractures.
- Occupational Therapy: Enhancing independence in daily activities.
Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention is key to managing symptoms effectively. Starting treatments and therapies as soon as possible can prevent irreversible damage and improve long-term outcomes. Collaborating with healthcare professionals and specialists is essential for developing a comprehensive care plan.
Role of Genetic Counseling
Genetic counseling plays a vital role in understanding SMA, managing expectations, and planning for the future. It provides families with information about the inheritance pattern, risk of recurrence, and available testing options. Genetic counselors can also help families navigate the emotional and psychological aspects of living with SMA.
Benefits of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing not only confirms a diagnosis of SMA but also provides valuable information about disease severity and treatment options. Identifying the number of SMN2 gene copies and detecting carrier status in family members can inform family planning and preventive measures.
Advancements in Research
Research into SMA continues to advance rapidly, with new treatments and therapies in development. Scientists are exploring innovative approaches, such as CRISPR gene editing, stem cell therapy, and small molecule drugs, to further improve outcomes for individuals with SMA.
Future Prospects
The future looks promising for individuals with SMA, with ongoing research focused on enhancing existing treatments and developing new therapies. Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and patient advocacy groups is driving progress and improving life expectancy and quality of life for those affected by SMA.
Support and Resources
Living with SMA can be challenging, but numerous resources are available to support individuals and families. These include:
- Non-Profit Organizations: Organizations like Cure SMA and the Muscular Dystrophy Association offer resources, support groups, and advocacy opportunities.
- Online Communities: Social media platforms and online forums provide spaces for sharing experiences and connecting with others.
- Clinical Trials: Participating in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments and contribute to advancing research.
Importance of Support Networks
Building a strong support network is essential for coping with the challenges of SMA. Connecting with others who understand the condition can provide emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of community.
Conclusion
Understanding the life expectancy of SMA requires a comprehensive approach that considers the type of SMA, access to treatment, and overall health management. Advances in medical science have transformed the outlook for individuals with SMA, offering hope and extending life expectancy for many. By staying informed, accessing available resources, and working closely with healthcare professionals, families can improve outcomes and quality of life for their loved ones.
We encourage readers to share this article, leave comments, or explore related content on our site. Together, we can continue to raise awareness and support those affected by SMA. Remember, knowledge is power, and every step forward brings us closer to a brighter future for all individuals living with SMA.